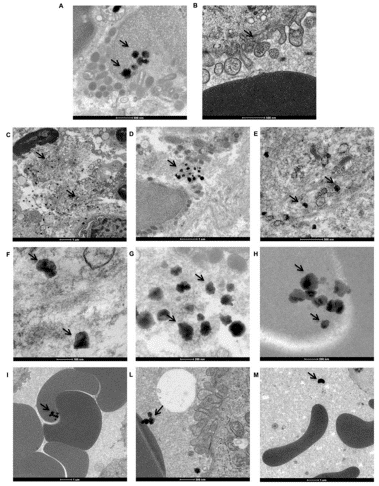
Recent data support the implication of accelerated titanium dissolution products in peri-implantitis. It is unknown whether these dissolution products have an effect on the peri-implant microbiome, the target of existing peri-implantitis therapies.
Author Archives: Administrator
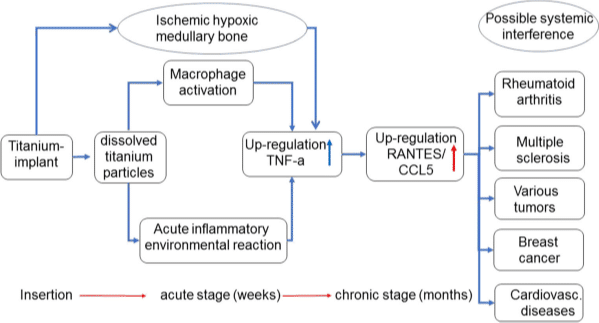
Ischaemic hypoxic medullary bone occurs when there is a disruption in the vascular supply of that bone tissue. Such disruption can occur when a thrombus (clot) is formed and does not subsequently break down (fibrinolysis).
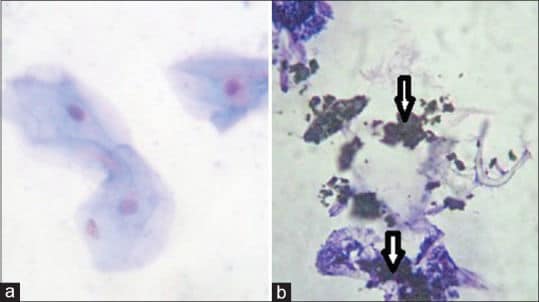
To evaluate the presence of titanium particles in the peri-implant mucosa of unloaded single implants.
All DTI (Dental Titanium Implant)-FDOJ (Fatty Degeneration with Osteonecrosis of the Jaw) samples showed RANTES/CCL5 (R/C) as the only extremely overexpressed cytokine. DTI-FDOJ cohort showed a 30-fold mean overexpression of R/C as compared with a control cohort of 19 healthy JB samples.
Titanium particles/ions detected in peri-implant tissues have been considered as a potential etiologic factor for crestal bone loss around oral implants. However, the definite impact of titanium wear particles on the health of surrounding structures remains undetermined.
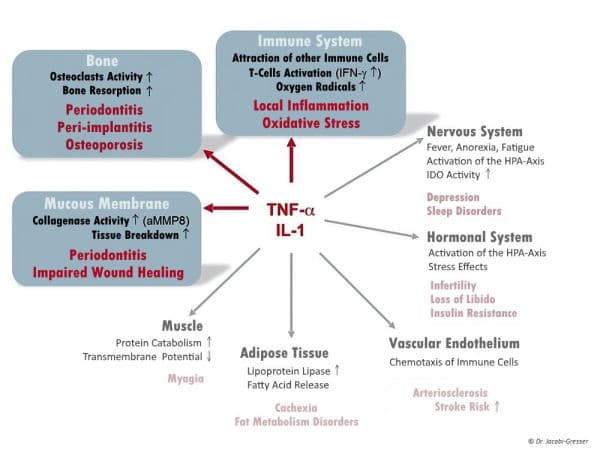
Peri-implantitis is a pathogenetically complex clinical picture and, in addition to local effects, has systemic effects depending on individual genetic susceptibility. It has some similarities to periodontitis but differs in the taxonomic biofilm composition and is also involved in foreign body reactions to the implant material.
The aim of this study is to identify the role of titanium nanoparticles released form the implants on the chronic inflammation and bone lysis in the surrounding tissue.
Epigenetic changes are associated with various inflammatory diseases and are influenced by environmental factors. Recent data support an association between titanium dissolution products and peri-implantitis.
Other relevant polymorphisms adversely impacting on bone health can increase the risk of peri-implantitis by affecting the rate of bone turnover, the bone mineral density and the formation of the collagen based bone matrix.
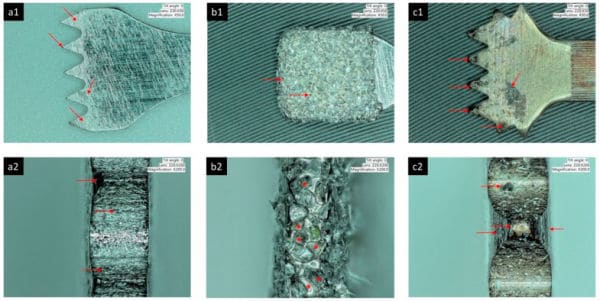
Implant surface characteristics, as well as physical and mechanical properties, are responsible for the positive interaction between the dental implant, the bone and the surrounding soft tissues.