Checkout Dr. Ignacio Vargas Gould, DDS, MSD Watch Video
Biography
- Doctor in Dental Surgery. Latin American University of Science and Technology, San Jose, Costa Rica. 1999-2004
- Division of Periodontics at Hospital Calderón Guardia. August 2002.
- Fellowship in Restorative Sciences , University of Costa Rica. 2004.
- Fellowship in Cosmetic Dentistry , University of Costa Rica. 2007.
- Master´s Degree in Operative and Dental Aesthetics, University of Costa Rica. 2008-2009
- Post-Doctoral Fellowship in Implant Dentistry, Pontificia University Javeriana, 2011.
- Digital Course in (Digital Smile Design). 2015
Certifications
- Basic Life Support. 2008 – Present
- National Dental Boards Examinations. 2004 – Present
- Course of Epidemiology and Biostatics for Health Professionals. Dr. Petri, May 2008
- Course of Peri-Implant Health and Management Hands – On Workshop. 2018
- Course of Implantology All on 4 (Oral Revitalize)
Professional Memberships
- Member of the Dental Surgeons College of Costa Rica. 2004 –Present
- Member of American Dental Association. 2011 – Present
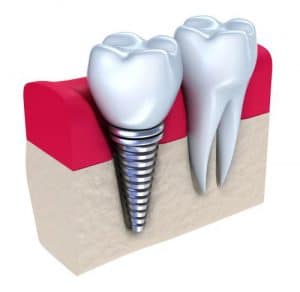
Dental implants
It happens. Losing teeth and then enduring the gap between your smile, affecting your ability to chew properly and even modifying your enjoyment of food and nutrition. This is why we wanted to let you know why Dental implants in Costa Rica are such a great option for you. When a tooth is lost, the jaw beneath that tooth begins to shrink and becomes fragile (due to lack of exercise). The loss of a tooth affects your smile and also changes the shape of your face, which makes it look prematurely aged. Thankfully there’s a solution for this problem. Dental implants can help you get back to your natural smile. They are used to replace missing teeth, keep your original bone structure, and youthful appearance. There are some some cases where dental implants won´t do it, so you may want to check out other dental treatments as the all on four.
Types of Dental Implants
Endosteal Implants:
Nowadays this is the type of dental implant most commonly used. These types of implants are placed surgically in the maxillary bones or in the jaw bone. When the implant is ready and the osseointegration is completed, the prosthesis or crown is placed to give it the appearance of a tooth.
There are several forms of the Endosteal implants: Cylindrical, Screw, Sheet, Titanium, Laminated, among others. This type of implants is generally used as an alternative for patients with bridges or dentures that are removable.
Subperiosteal or Juxta-Osseous Implants:
These types of implants consist of a metal frame that is placed in the jaw bone just below the gum tissue. Therefore, these have the shape of the edge of the bone so that they can be properly fixed.
Mainly, these types of dental implants are used for patients who can not use conventional dentures and who have a minimum bone height so it is not possible to use an endosteal implant
Bone graft and membrane
After a tooth is extracted, healing of soft tissues and bone follows. Without preservation of the extraction site, the bone surrounding the extracted socket space gradually resorbs, resulting in soft and hard tissue defects. This reduction in quantity & quality of bone, is a source of problem for future treatment options like dental implants or prostheses, affecting their functional and esthetic outcomes.
Although the process of resorption of dental ridges after extraction is unpredictable, predominant horizontal bone loss affecting the buccal bone of the ridge is the pattern majorly observed. Due to this resorptive pattern, a lingually inclined, atrophied ridge is the result.
To combat these hard and soft tissue defects after tooth extraction, bone grafting for site preservation is the solution.
Research has shown that the sockets preserved with bone grafting on average lost 2 mm less of ridge width, 1 mm less of ridge height, and were found to have 20% more bone volume compared to sockets that were not grafted.
Bone Grafts
Bone grafts acts as a framework facilitating and inducing the generation of new bone. It acts as a mineral reservoir and has no antigen-antibody reaction.IT is a procedure that utilizes either a natural or synthetic substitute for replacing the resorbed or lost bone. On the basis of materials used in bone grafting, it can be classified as follows.
Types of Bone grafts
- Allograft-based bone graft involves taking tissue from one individual to another individual of the same species
- Factor-based bone graft they are natural growth factors used alone or in combination with transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), fibroblast growth factors (FGF), and bone morphogenic protein (BMP).
- Cell-based bone grafts use cells to generate new tissue alone or can be added to a support matrix, like mesenchymal stem cells.
- Ceramic-based bone graft substitutes including calcium phosphate & calcium sulfate can be used alone or in combination
- Polymer-based bone grafts use degradable and nondegradable polymers alone or in combination with other materials
Indications for Bone grafting
Dental Implants- The most common application of bone grafting for dental implants. Implants need a healthy bone in an adequate amount for reintegration. Bone grafting is the best option to restore the edentulous area where a sufficient amount of bone is absent.
Sinus lift graft is the procedure involving elevation of the sinus membrane and grafting bone onto the sinus floor, for secure placement of the implants.
Ridge augmentation – Defects in the dental ridge can occur due to trauma, injury, severe periodontal disease or congenitally. The bone graft can fill the ridge and jawbone uniformity is obtained
Nerve repositioning –Sometimes mandibular implants requires movement of the inferior alveolar nerve to allow for the placement of implants, a bone grafting procedure might help in this case.
Membranes
RESORBABLE MEMBRANES:
One of the materials used for resorbable membranes is Collagen. It is a heavily cross-linked protein which makes it an efficient barrier.
PRF is another leading source to create a durable resorbable membrane that tends to last 7-14 days. It utilizes platelet-rich fibrin ( Fibrin is a protein involved in blood clotting). It is made by the process of centrifugation. PRF has stretched out, slimy consistency that protects the graft. These membranes can be used in addition to other resorbable or non-dissolvable membranes for dental implant bone grafts.
NON-RESORBABLE MEMBRANES:
Most non-resorbable membranes are made of titanium or Dense polytetrafluoroethylene. (PTFE).To hold the membrane in place and to ensure that it keeps the bone graft covered, PTFE is often used with bone tacks.
One benefit of a non-resorbable membrane is its predictability for successful bone generation. The downside is that it has to be removed at a second procedure. The process of membrane removal might differ from case to case. It can be removed by simply plucking it out of the socket, over the graft, or it might take a longer procedure involving reopening the gums, removal of bone tacks followed by membrane removal.
Titanium reinforced membranes, or titanium mesh, is best at holding space. by preventing your gums from collapsing & enabling the buildup of new volume and mass underneath.