Immediate implantation: Ceramic implants in the lower jaw posterior region
By Dr. Saurabh Gupta BDS, MDS
Ceramic implants have become firmly established in dental implantology. Patient demand for metal-free solutions is increasing, and the development of new biomaterials, microrough surface techniques and improved treatment protocols have enabled practices to use zirconia dental implants as a reliable treatment alternative to titanium implants. In this case report, the replacement of a mandibular posterior tooth with a zirconium oxide implant is described.
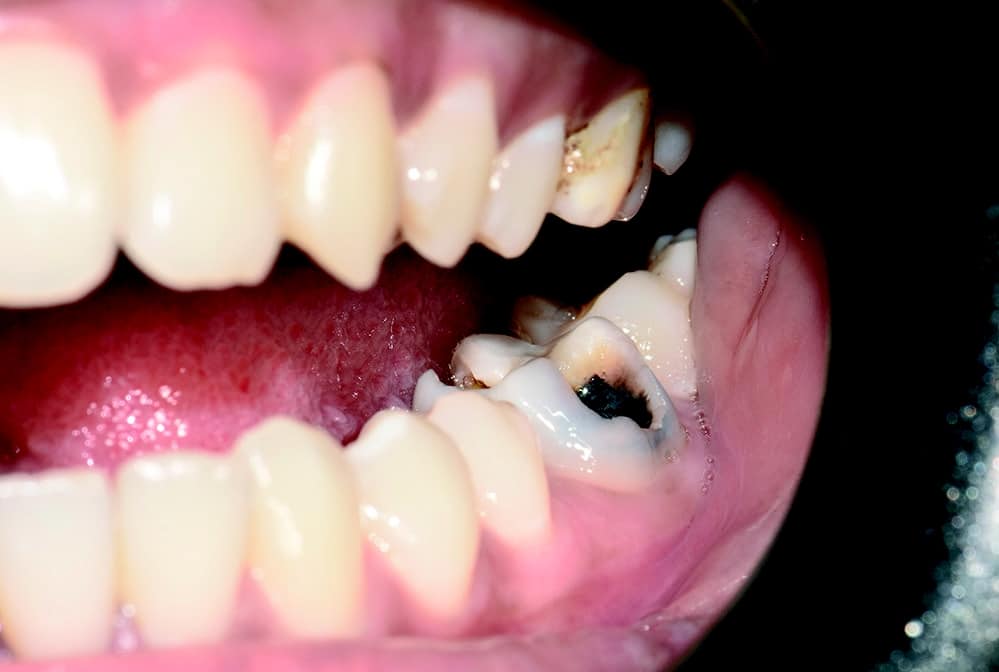
Several studies have shown and proven that zirconia implants cause little to no inflammation of the peri-implant tissue cause – with a simultaneous lengthening of the epithelial attachment. In addition, these implants look more natural and therefore offer improved aesthetics. In addition, they contain no metal components, making them ideal for patients with metal sensitivity or preferences for a metal-free solution. The patient should be informed about the advantages and disadvantages of both material options and included in the decision-making process when a zirconia implant is offered as a treatment option [1-5]. Clinical situation and treatment planning A 21-year-old healthy patient presented to our clinic. She requested a permanent solution for her endodontically infected molar (Fig. 1a).
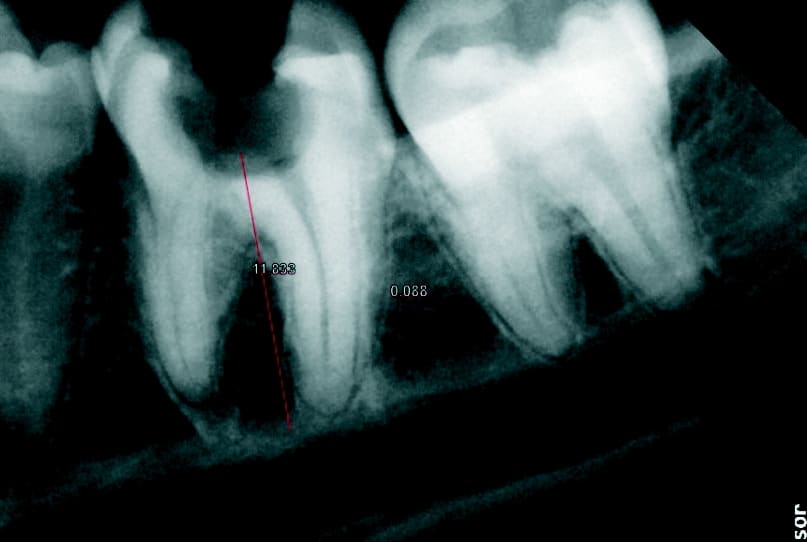
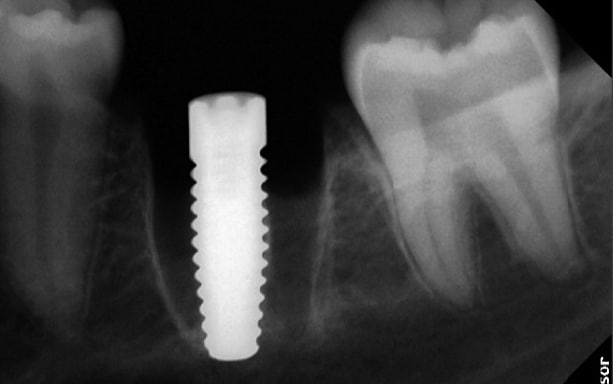
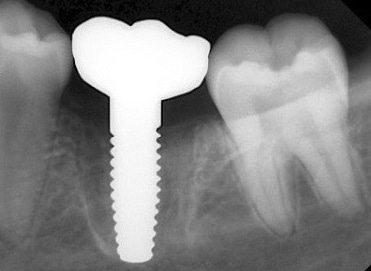
The molar (tooth 36) had been endodontically treated six months previously. X-ray revealed a fracture related to tooth 46 (Fig. 1b). The fractured molar 36 was scheduled for extraction. The patient was informed about ceramic implants as an alternative to titanium implants and the Zeramex XT dental implant as a metal-free solution. After a detailed explanation and discussion, the patient decided on this treatment option. The main reason for their decision was the prognosis of less inflammation of the peri-implant tissue with ceramic implants and a metal-free solution. Surgical and restorative protocols After extraction of tooth 36, curettage and laser debridement (Biolase diode laser, 940 nm) of the socket were performed (Fig. 2). The x-ray showed few remnants of PDL around the alveolus.
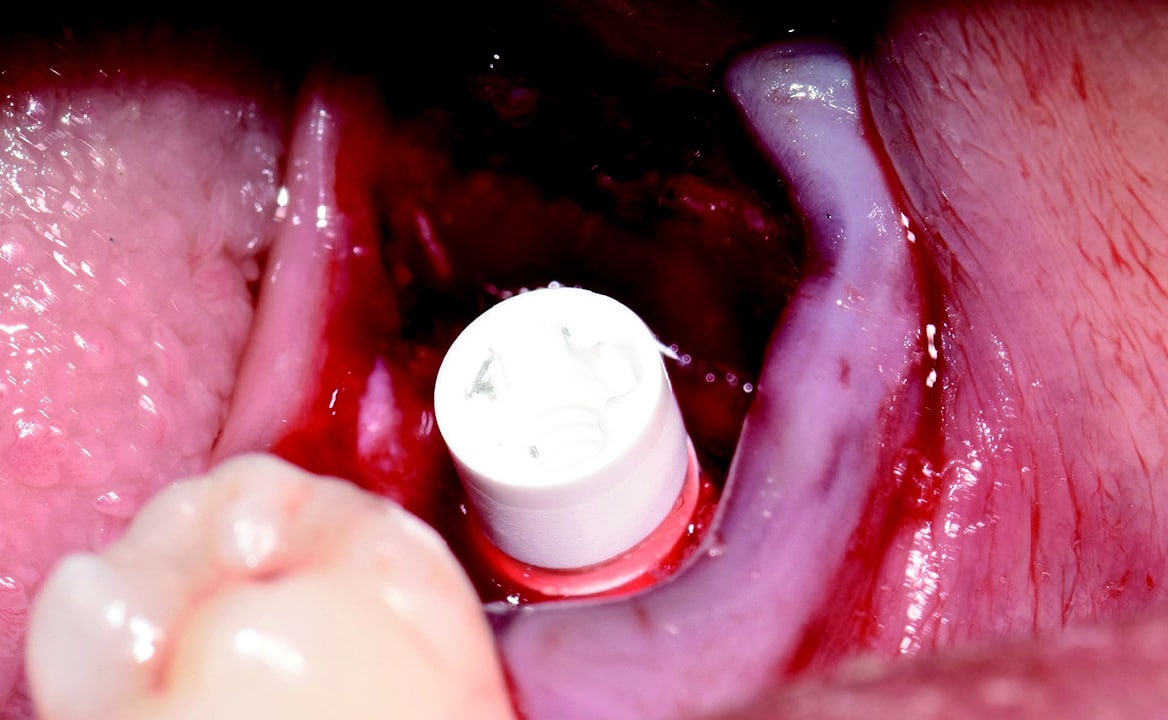
Around the immediate implants, the preserved PDL residues contributed directly to new bone formation and osseointegration (Fig. 3) [6]. The surgical guidelines of the drilling protocol were followed and a two-piece zirconia dental implant (Zeramex XT) measuring 4.2 x 12mm was used to replace tooth 36 (Figs. 3 and 4). The implant was inserted with a torque of 35 Ncm in the interdental bone with a supragingival connection level (1.6 mm). The transgingival shoulder with its smooth surface (0.6 mm) offers the optimal conditions for the adhesion of soft tissue. Primary stability has been achieved. The implant was covered with an end cap in situ and the site sealed without transplantation.
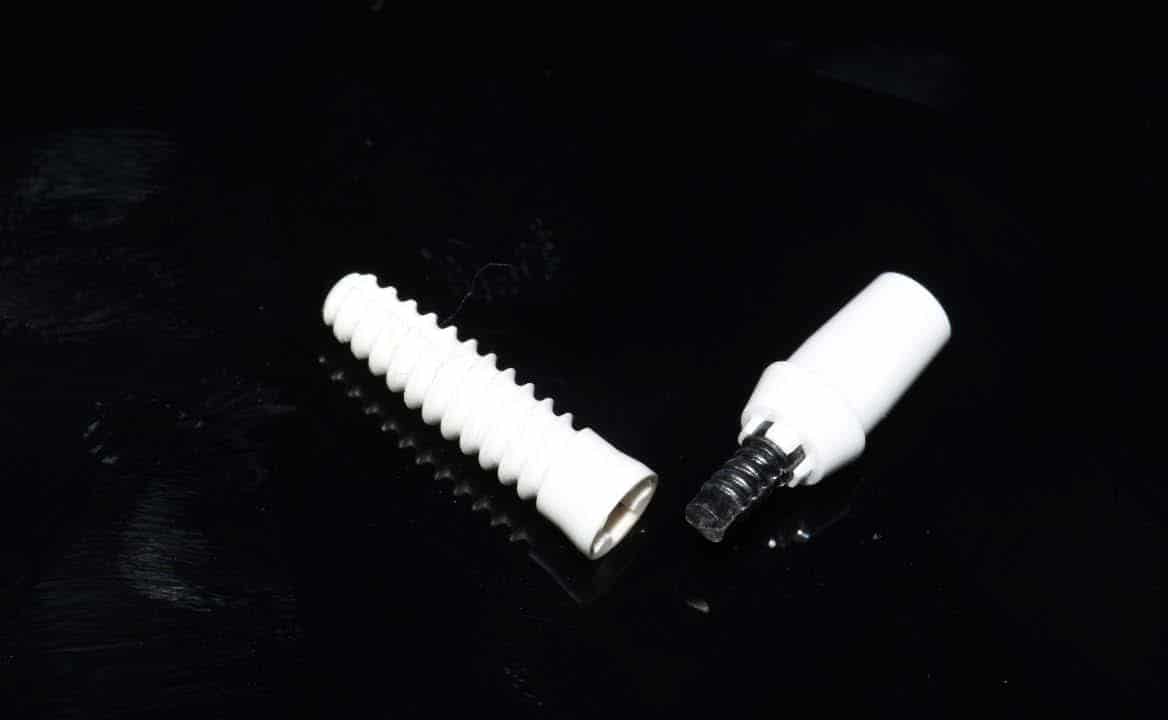

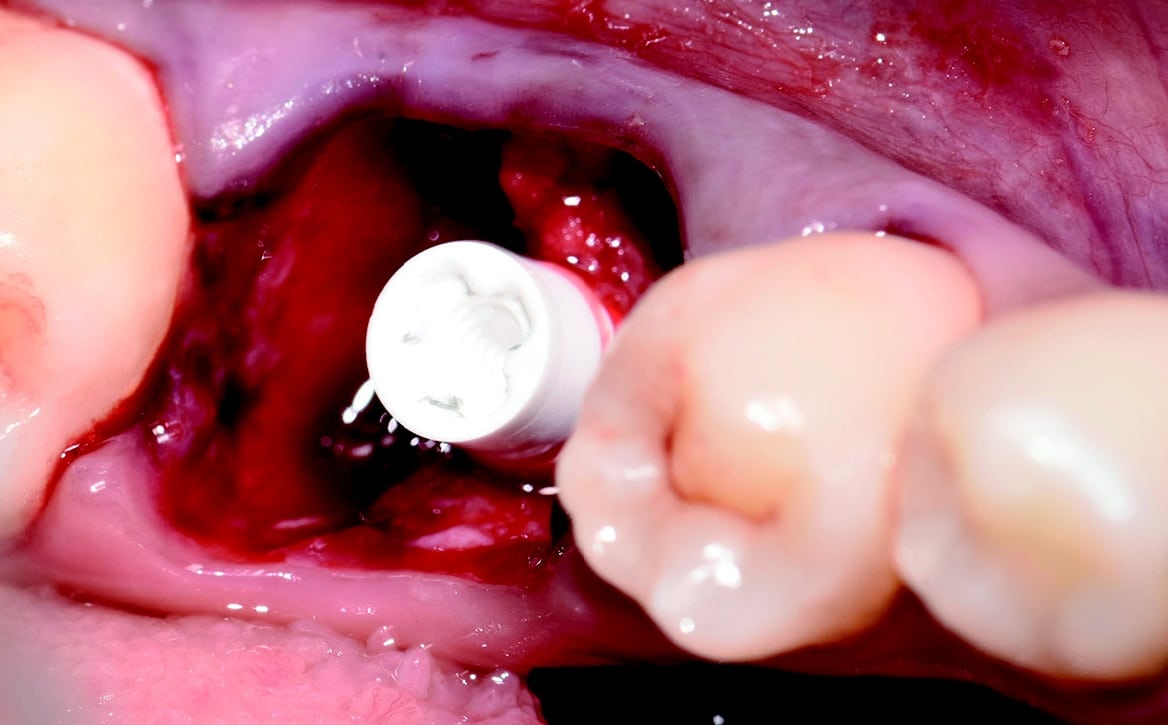
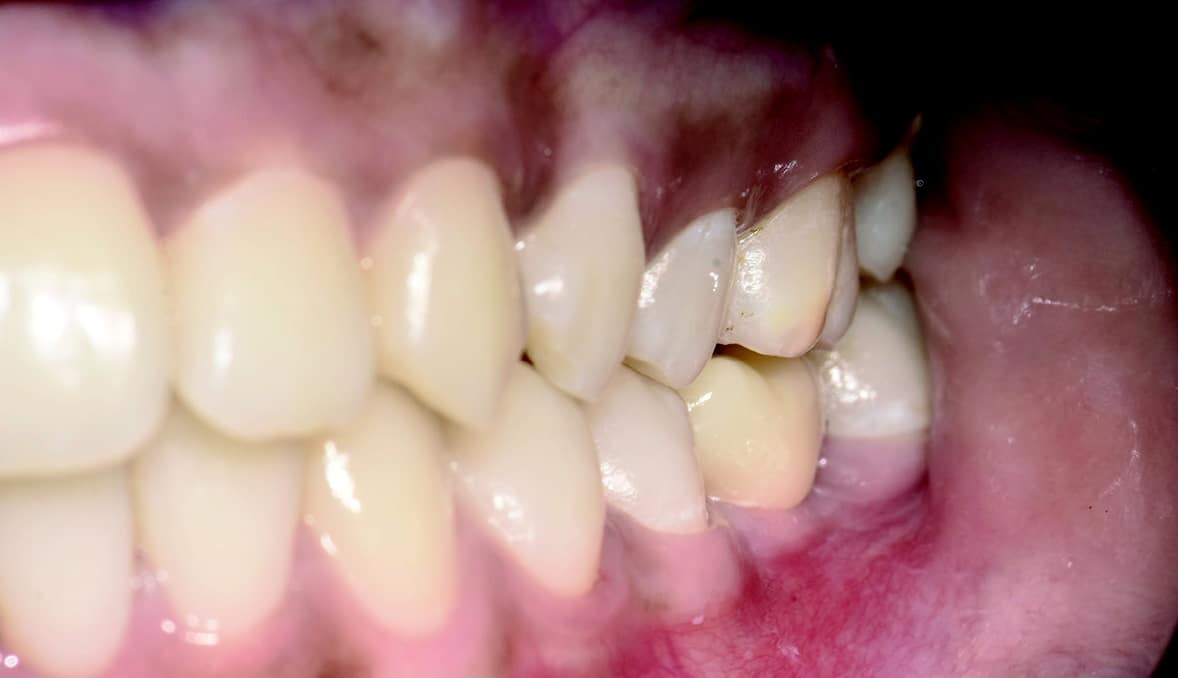
Four months after surgery, the restorative process began with removal of the end cap and placement of a straight zirconia abutment with a carbon fiber screw (Figs. 5 and 6). The abutment was screwed with a torque of 25Ncm for a permanent abutment-implant connection. The height of the abutment was adjusted using a Rotring diamond bur, followed by a conventional impression procedure for the final restoration. Procedure for the final supply. The soft tissue around the abutment was healthy and keratinized when the impression was taken. A monolithic zirconia crown was used as the prosthetic solution. In order to achieve a tension-free and bending free connection between the restoration and the implant, the zirconia restoration was cemented intraorally onto the abutments using the standard procedure with glass ionomer cement (Shofu INC, Japan) (Fig. 7).
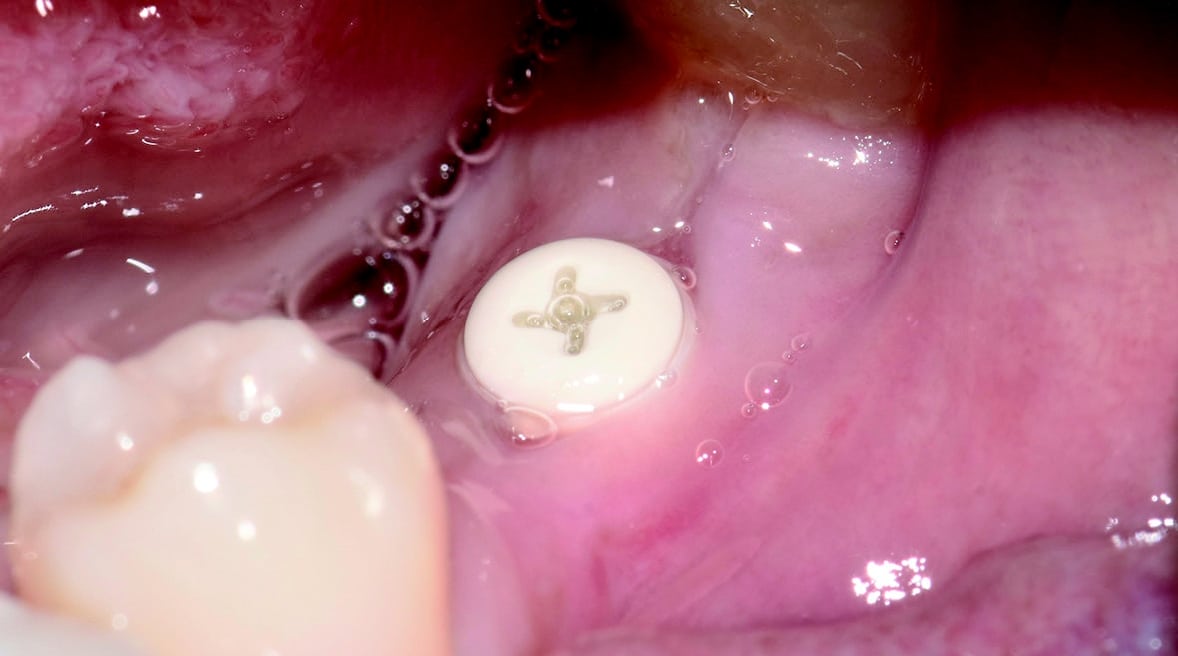
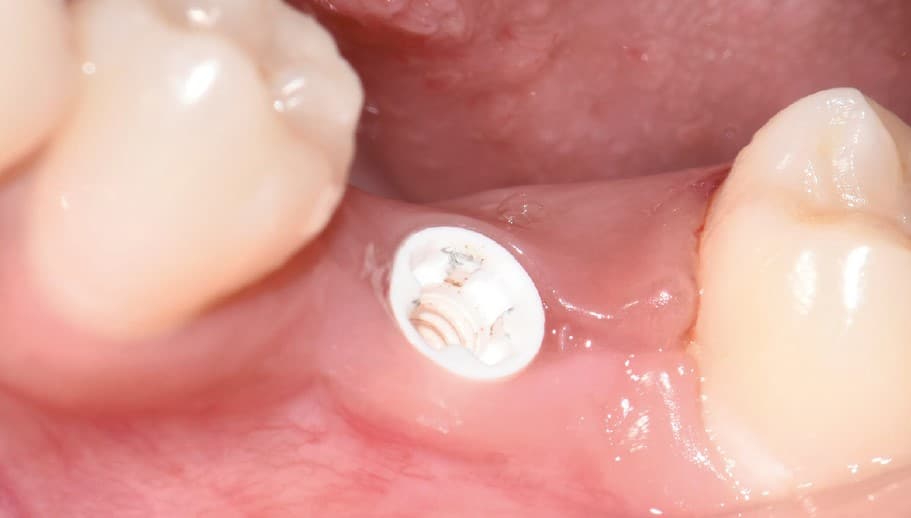
Clinical Outcomes
The result was beautiful with excellent tissue healing. The patient was very satisfied. No inflammation or prosthetic problems occurred during the follow-up period. The result in this case was a 100% metal-free implant and a metal-free crown.
Conclusion
The Zeramex XT implant system is designed for a wide range of indications, from single implants to multiple implants.
In the case presented, it has proven to be excellent as an immediate implant for the infected alveolus. The surgical and prosthetic protocols are comparable to those of titanium implants. These are important factors for the successful integration of a new implant system into everyday practice. Our main reasons for using Zeramex XT in the case presented were the following:
- The Zeramex XT implant system is designed to support a natural soft tissue appearance, particularly in patients with a thin mucosal biotype.
- Zirconia generally exhibits lower plaque accumulation and bacterial adhesion than titanium.
- The Zerafil surface of these implants is microrough and hydrophilic for successful
osseointegration, while the implant collar is partially machined to ensure excellent soft tissue
attachment and a low inflammatory response. - These implants also offer an advantage in mechanical strength. They are made of ATZ zirconia (aluminum-toughened zirconia), which offers improved hardness, flexural strength and toughness.
- The implants offer great restorative flexibility thanks to their two-piece design with internal
connection. - Micro-threads in the cortical bone area allow for better primary stability and axial loading, and
the clinical protocol is comparable to that of titanium implants. - It is a metal-free solution with a strong, tension-reducing Vicarbo screw that ensures an optimal implant-abutment connection.
DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY | Year 26 | Issue 04 | June 2022 | 218-221
Pictures, unless otherwise stated: © Gupta
About the Doctor
Dr. Saurabh Gupta
FOUNDER AND DIRECTOR, WHITEZ DENTAL CLINIC EDUCATION DIRECTOR, IAOCI, USA
Dr. Saurabh Gupta has a Master’s Degree in Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery from RGYHS College, Bangalore. He completed his graduation at the renowned Manipal College of Dental Science, Manipal, India. He is a trained professional in multiple surgical disciplines, which include Digital and Laser Dentistry and Implantology.
He is an international and national lecturer and is the Board Member/Education Director of ‘The International Academy of Ceramic Implantology.’ This academy is the USA’s first body to work on metal-free implantology.
He is a dynamic personality and a member of The Zirconia Implant research Group (ZIRG), which aims to orient and lead research work in the field of metal-free implantology and provide support to established and young clinicians in scientific and clinical research. He is an indispensable part of the ‘Bio-ceramic Division’ at ‘The American Ceramic Society,’ Ohio, US. He is also the Academic Collaborator at IISc (The Indian Institute of Science), Bangalore, working on several significant Research and Development projects.
He is also the ambassador and fellow at ‘The Cleaning Implant Foundation, Germany,’ and the body aims at assessing the quality of products and cleanliness of implant surfaces that are available in the commercial markets. He is a member of the advisory board for ‘The Journal of Oral Ceramic Implantology’ (ISSN2293-7897). He is the clinical specialist at COHO Biotechnology, Taiwan. Currently, he is actively working on several research studies focusing mainly on digital dentistry and implant materials.

WhiteZ Dental, Bangalore, India | + 91 99 1620 3455 | saurabh.ravzz@gmail.com | saurabh@iaoci.com
Contact
Want to know more about Zeramex?
Email us at mfoley@zeramexusa.com with your contact details and we will get in touch with you!
ZERAMEX BROCHURE
Click here to download the Zeramex sales brochure