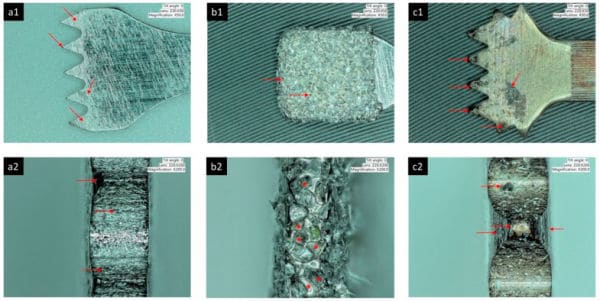
Implant surface characteristics, as well as physical and mechanical properties, are responsible for the positive interaction between the dental implant, the bone and the surrounding soft tissues. Unfortunately, the dental implant surface does not remain unaltered and changes over time during the life of the implant. If changes occur at the implant surface, mucositis and peri-implantitis processes could be initiated; implant osseointegration might be disrupted and bone resorption phenomena (osteolysis) may lead to implant loss. Titanium particle and ions are released during the implant bed preparation, during the implant insertion and during the implant decontamination. In addition, the implant surfaces and restorations are exposed to the saliva, bacteria and chemicals that can potentially dissolve the titanium oxide layer and, therefore, corrosion cycles can be initiated. Mechanical factors, the micro-gap and fluorides can also influence the proportion of metal particles and ions released from implants and restorations.