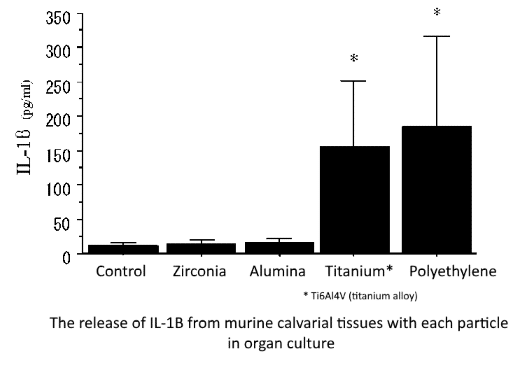
The inflammatory response and bone resorption induced by ceramic particles were much smaller than those induced by polyethylene and Ti6Al4V. These biological features suggest the biocompatibility of ceramics as a joint surface material for artificial joints.